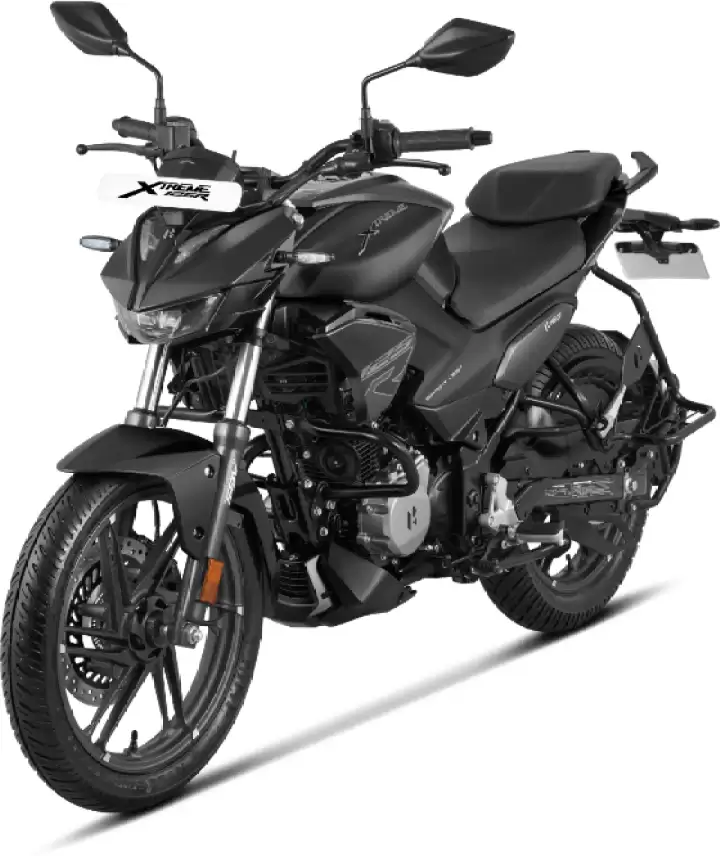
Hero Xtreme 125R एक ऐसी बाइक है, जो पावर, स्टाइल और कंट्रोल का बेहतरीन मिश्रण पेश करती है। यह बाइक अपने सेगमेंट में पहली बार Single-Channel ABS के साथ आती है, जो आपको बेहतर ब्रेकिंग पावर देता है और अनएक्सपेक्टेड Situations में भी आपको फुल कंट्रोल में रखता है। इसका नया इंजन एड्रेनालिन-फ्यूल्ड परफॉर्मेंस के साथ आता है, जो आपको हर चुनौती को आसानी से पार करने का कॉन्फिडेंस देता है।
चलिए इस शानदार बाइक की सभी खासियतों को विस्तार से समझते हैं।

Hero Xtreme 125R’s Powerful Engine
Hero Xtreme 125R का All New Engine sheer thrills के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया है। 124.7cc का इंजन 8.5 kW @ 8250 rpm का मैक्सिमम पावर और 10.5 Nm @ 6500 rpm का टॉर्क जेनरेट करता है। इसकी Fuel Injection Technology न सिर्फ परफॉर्मेंस बढ़ाती है, बल्कि इसे ज्यादा एफिशिएंट भी बनाती है।

Broad Rear Tire for Controls
Hero Xtreme 125R के Wide Rear Tire (120/80X17) के साथ आप हर मोड़ पर खुद को पूरी तरह से कंट्रोल में पाएंगे। यह टायर सिर्फ परफॉर्मेंस नहीं बढ़ाता, बल्कि आपकी राइड को स्टाइलिश भी बनाता है।

Hero Xtreme 125R: Monoshock Suspension
SHOWA का Monoshock Suspension इस बाइक की सबसे बड़ी खासियत है। चाहे सड़क कितनी भी खराब क्यों न हो, यह सस्पेंशन स्मूद राइड की गारंटी देता है। इससे आप हर चुनौती को आरामदायक तरीके से पार कर सकते हैं।
Full LED Setup with Hero Xtreme 125R
Hero Xtreme 125R सेगमेंट में पहली बार, Full LED Setup के साथ आने वाली यह बाइक आपके रास्ते को रोशन करने के साथ-साथ दूसरों का ध्यान भी खींचती है। Projector Beam, LED Blinkers, और Bold Taillight इसे रात में और भी शानदार बनाते हैं।

Specifications
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | Fuel Injection (FI) |
| Displacement | 124.7 cc |
| Power | 8.5 kW @ 8250 rpm |
| Torque | 10.5 Nm @ 6500 rpm |
| Transmission | 5-Speed |
| Rear Tire | 120/80X17 Tubeless |
| Braking System | Front Disc, Rear Drum |
| Lighting | Full LED with Projector Beam |
| Mileage | 43 km/l (Standard), 60-62 km/l (after second service if ridden under 50 km/hr for initial 1500 km) |
Also check: Samsung Galaxy Z Flip6: A Game-Changer Powerful Smartphone

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: कितने किलोमीटर प्रति लीटर का माइलेज है?
A: यह बाइक स्टैंडर्ड कंडीशन में 43 km/l का माइलेज देती है। सेकंड सर्विस के बाद और 50 km/hr से कम स्पीड पर चलाने पर यह माइलेज 60-62 km/l तक पहुंच सकता है।
Q: स्टैंडर्ड एक्सेसरीज़ में क्या मिलता है?
A: लेग गार्ड, मिरर्स और साइड स्टैंड स्टैंडर्ड एक्सेसरीज़ में शामिल हैं।
Q: बाइक पर दो लोगों का वजन कितना लिया जा सकता है?
A: बाइक आसानी से 200 kg तक का वजन संभाल सकती है।
Q: रियर टायर का ब्रेक सिस्टम कैसा है?
A: रियर टायर में ड्रम ब्रेक दिया गया है।